Rare Case Of Three Kidneys Reported In NEJM
- byDoctor News Daily Team
- 23 July, 2025
- 0 Comments
- 0 Mins
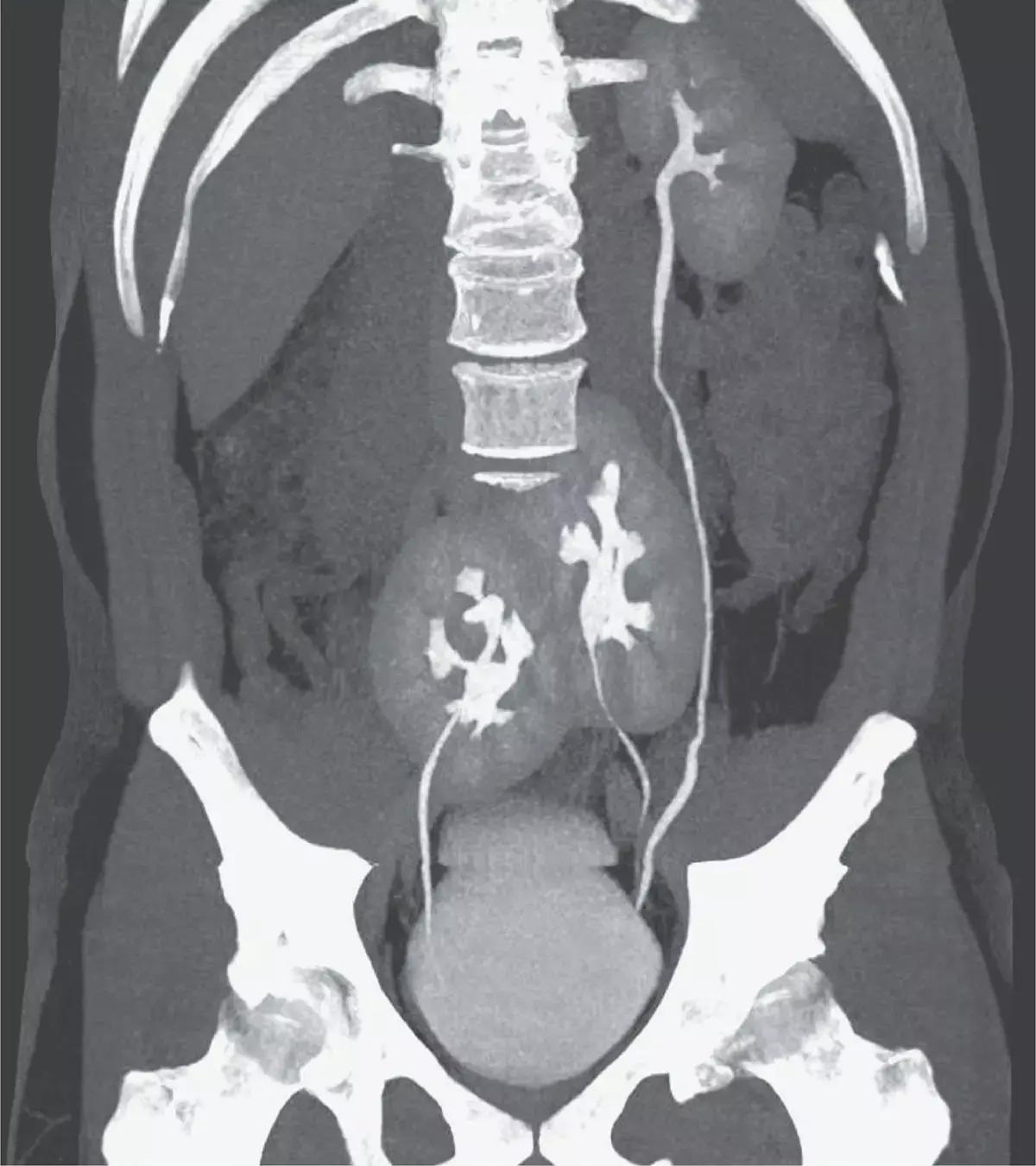
Dr Jose O. Medina-Pestana and Dr Renato D. Foresto at Hospital do Rim, São Paulo, Brazil have reported a rare case with three kidneys.The case has appeared in the New England journal of Medicine.
Three kidneys are relatively uncommon and are usually discovered by accident bect they rarely cause symptoms. It usually means that one of the kidneys were split into two prior to birth. It can be associated with infections and kidney stones, but usually causes no symptoms.
Computed tomography is the method of choice for visualizing Supernumerary kidneys. The correct diagnosis is crucial in preventing dispensable surgical procedures and for providing optimal patient treatment and outcomes.
According to the history a 38-year-old man presented to the outpatient clinic with severe low back pain. As part of the evaluation, computed tomography (CT) was performed. The scan incidentally showed the presence of three kidneys: a normal-appearing left kidney and two fused kidneys in the pelvis. The ureter from the left pelvic kidney joined the ureter from the other left kidney just above its entrance into the bladder. The ureter from the right pelvic kidney entered the bladder on the right side. The CT scan also showed a herniated disk between L4 and L5. Renal function was normal, with a creatinine level of 0.9 mg per deciliter (80 μmol per liter) (normal range, 0.6 to 1.0 mg per deciliter [53 to 88 μmol per liter]). This uncommon congenital abnormality was thought to be the consequence of aberrant processes during embryogenesis. The duplicate left kidney may have resulted from a premature division of the left ureteral bud. In addition, the right and lower left developing kidneys fused and did not ascend during development. Affected persons are commonly asymptomatic, and as in this case, the condition may not become known until imaging is performed for another reason. The patient's back pain was attributed to the lumbar disk herniation, and he was treated with an oral analgesic agent.
For further reference log on to:
N Engl J Med 2020; 382:1843
DOI: 10.1056/NEJMicm1910376
Disclaimer: This website is designed for healthcare professionals and serves solely for informational purposes.
The content provided should not be interpreted as medical advice, diagnosis, treatment recommendations, prescriptions, or endorsements of specific medical practices. It is not a replacement for professional medical consultation or the expertise of a licensed healthcare provider.
Given the ever-evolving nature of medical science, we strive to keep our information accurate and up to date. However, we do not guarantee the completeness or accuracy of the content.
If you come across any inconsistencies, please reach out to us at
admin@doctornewsdaily.com.
We do not support or endorse medical opinions, treatments, or recommendations that contradict the advice of qualified healthcare professionals.
By using this website, you agree to our
Terms of Use,
Privacy Policy, and
Advertisement Policy.
For further details, please review our
Full Disclaimer.
Recent News
Eli Lilly plans to build new USD 3 billion facilit...
- 04 November, 2025
Rajkot Maternity Hospital CCTV Leak: How a simple...
- 04 November, 2025
Gland Pharma profit rises 12 percent to Rs 184 cro...
- 04 November, 2025
AIIMS Delhi doctors told to use Hindi in prescript...
- 04 November, 2025
Daily Newsletter
Get all the top stories from Blogs to keep track.


0 Comments
Post a comment
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!